Does Image Size Matter? The Truth About Resolution & Quality

Do you encounter problems with blurry images, pixelation, and slow file loading when designing for the web, printing photos, or sharing visuals on social media? These problems are all related to image size and resolution. Contrary to popular belief, bigger is not always better.
The right image size ensures clarity, fast load times, and optimal performance across platforms. That's why we need to choose the right image size or resolution for different purposes.
Let's start by understanding the science behind image resolution and how it affects quality. Then, we optimize the image in a good way without losing details.

Breaking Down Image Size & Resolution
- What is image size?
Image size refers to the dimensions and file weight of an image, usually measured in the following units:
- Pixels (px): The number of horizontal and vertical dots in an image
- Inches (in) and centimeters (cm): for print formats
- kilobytes (KB) and megabytes (MB): file weight, which affects storage and loading times
- What is image resolution?
- Pixels per inch (PPI): determines the sharpness of a digital image
- Dots Per Inch (DPI): relates to printed images
The higher the resolution, the greater the detail, but also the larger the file size.

- Image Quality: More than just pixels
- Compression: Reducing file size without sacrificing quality (JPEG vs. PNG vs. WebP)
- Color Depth: The number of colors that can be displayed in an image
- File Format: Determines quality, transparency, and compression.
Here’s a cleaner and more structured way to present your content:
The Science of Image Clarity
- The Role of Pixels: How Many Do You Really Need?
- Megapixel Myth: Higher megapixels don’t always mean better quality.
- Print vs. Digital: The pixel count required varies between screens and prints.
- The Impact of Compression: Saving Space vs. Losing Quality
| Compression Type | Effect | File Size |
| Lossy (JPEG) | Reduces size but sacrifices detail | Smaller |
| Lossless (PNG/WebP) | Maintains detail but results in larger files | Larger |
- Display vs. Print: Why Resolution Requirements Differ
| Usage | Recommended Resolution |
| Web Images | 72-150 PPI |
| Print Images | 300 DPI minimum |

Bigger vs. Smaller Images: Pros and Cons
- When Bigger is Better
Larger images are better at maintaining high-quality professional printing and photography. They ensure clarity and detail in large displays such as billboards, posters, and high-resolution monitors where every pixel counts. High-resolution images can also be cropped and resized without a noticeable loss of quality.

- When Smaller is Smarter
Smaller images help to speed up website loading and improve SEO rankings and user experience. They are especially useful for mobile optimization and social media, where fast loading and efficient storage are key.
Additionally, compressing images reduces bandwidth usage, making them ideal for improving website and app performance.
- Finding the Sweet Spot: Optimizing for Purpose
Choosing the right image size depends on its intended use - web, print, or social media. For web platforms, resizing and compressing images without sacrificing too much quality is the key to achieving a balance. TinyPNG and imglarger's Resize feature helps optimize images, reducing file size while maintaining visual appeal.

How Image Size Affects Performance
The Web Performance Factor
Google's core website lifecycle emphasizes that fast-loading images are a key ranking factor for search engine optimization and user experience. Large, unoptimized images slow down websites, increase load times, and frustrate users. Optimizing file size can help reduce bounce rates, keep visitors engaged, and increase conversions.

Social Media Impact: Why Platforms Resize Your Images
Social media platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter automatically compress images to maintain faster loading speeds. Due to platform compression, uploading too large photos may result in lower-quality images. Using the optimal size for each platform ensures better display quality:
- Instagram: 1080×1080px (square posts)
- Facebook: 1200×630px (shared images)
- Twitter: 1600×900px (tweets with images)

The SEO Angle: Can Image Size Hurt Your Rankings?
Image size plays an important role in search engine rankings, as fast-loading pages perform better on Google. Excessively large images can slow down a website and negatively impact search engine optimization.
Optimizing images with proper ALT text and descriptive filenames improves discoverability, making them more accessible to search engines and users.

File Formats & Their Role in Image Quality
JPEG vs. PNG vs. WebP: Which One to Use?
Different image formats serve different purposes, balancing quality, compression, and transparency. Choosing the right format is essential for optimizing performance and visual fidelity.
| Format | Compression | Transparency | Best Use Case |
| JPEG | Lossy | No | Web & photography (small file size, good quality) |
| PNG | Lossless | Yes | Logos & transparent images (sharp details) |
| WebP | Both | Yes | Modern web optimization (better compression, high quality) |
WebP is becoming the preferred choice for websites due to its balance between quality and compression, making pages load faster while maintaining sharp visuals.
RAW vs. TIFF: The Professional's Choice
- RAW files capture unprocessed image data directly from a camera sensor, allowing maximum flexibility for post-processing. They preserve all details, making them ideal for professional photographers and editors.
- TIFF files retain high quality with minimal compression, making them perfect for professional printing. Unlike RAW, TIFF files are widely supported across editing software and print media, ensuring consistency in color and detail.
How to Resize an Image Without Losing Quality with Imglarger
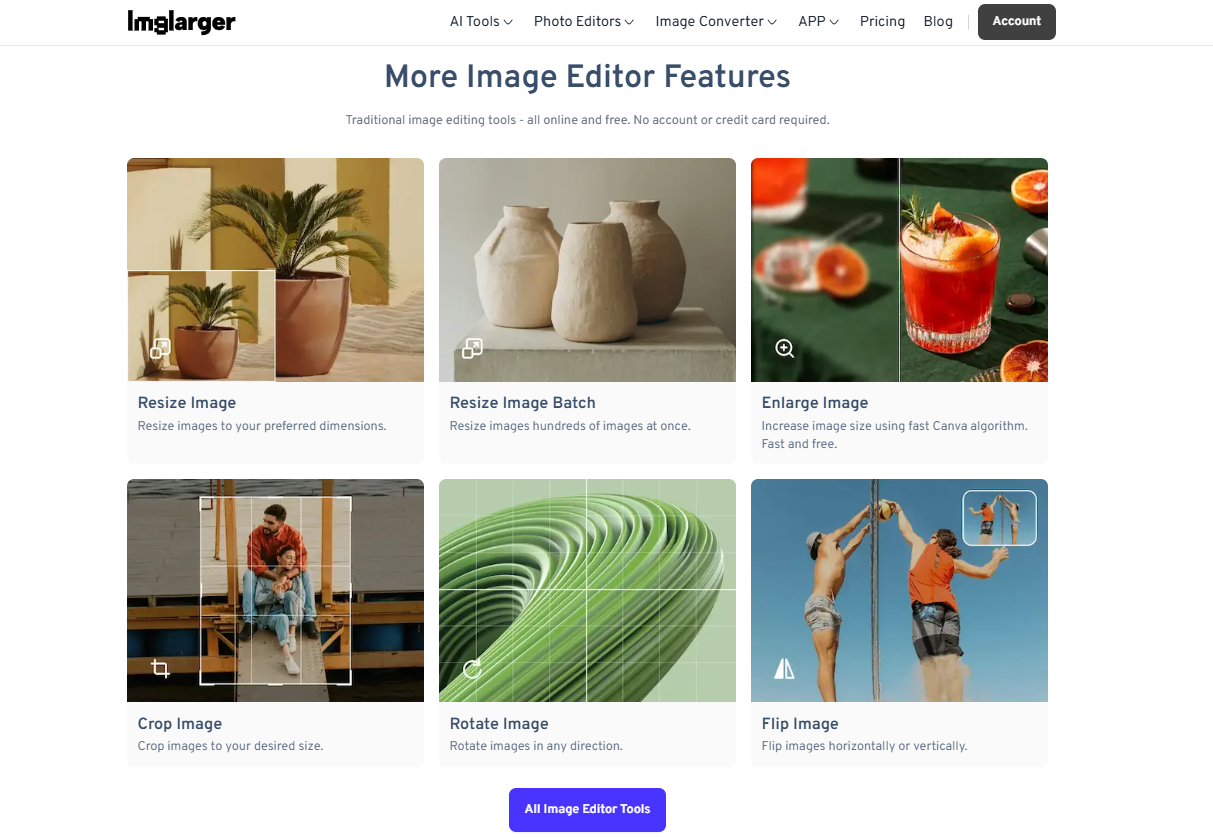
- Step 1: Go to Imglarger's homepage and scroll down to select Resize Image in More Image Editing Tools.
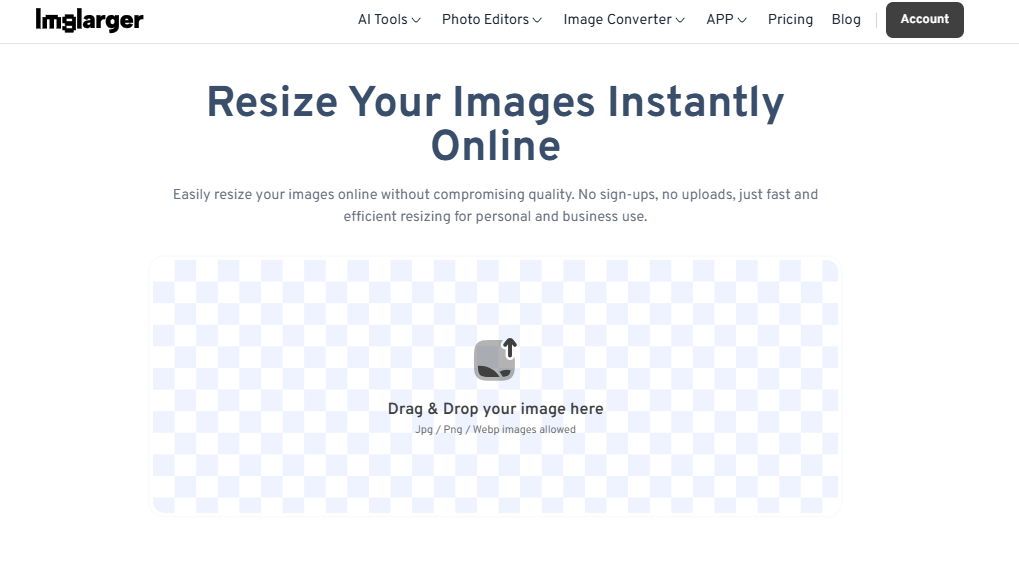
- Step 2: After entering the page, you can click or drag and drop to upload the photos you need to resize, and then enter the editing page after uploading. Select "Resize" in the last box on the left side of the page.
- Step 3: After clicking it, we can see two boxes below the picture; you can customize the length and width according to your own needs or click the lock in the middle of the two boxes to lock the ratio of length and width.
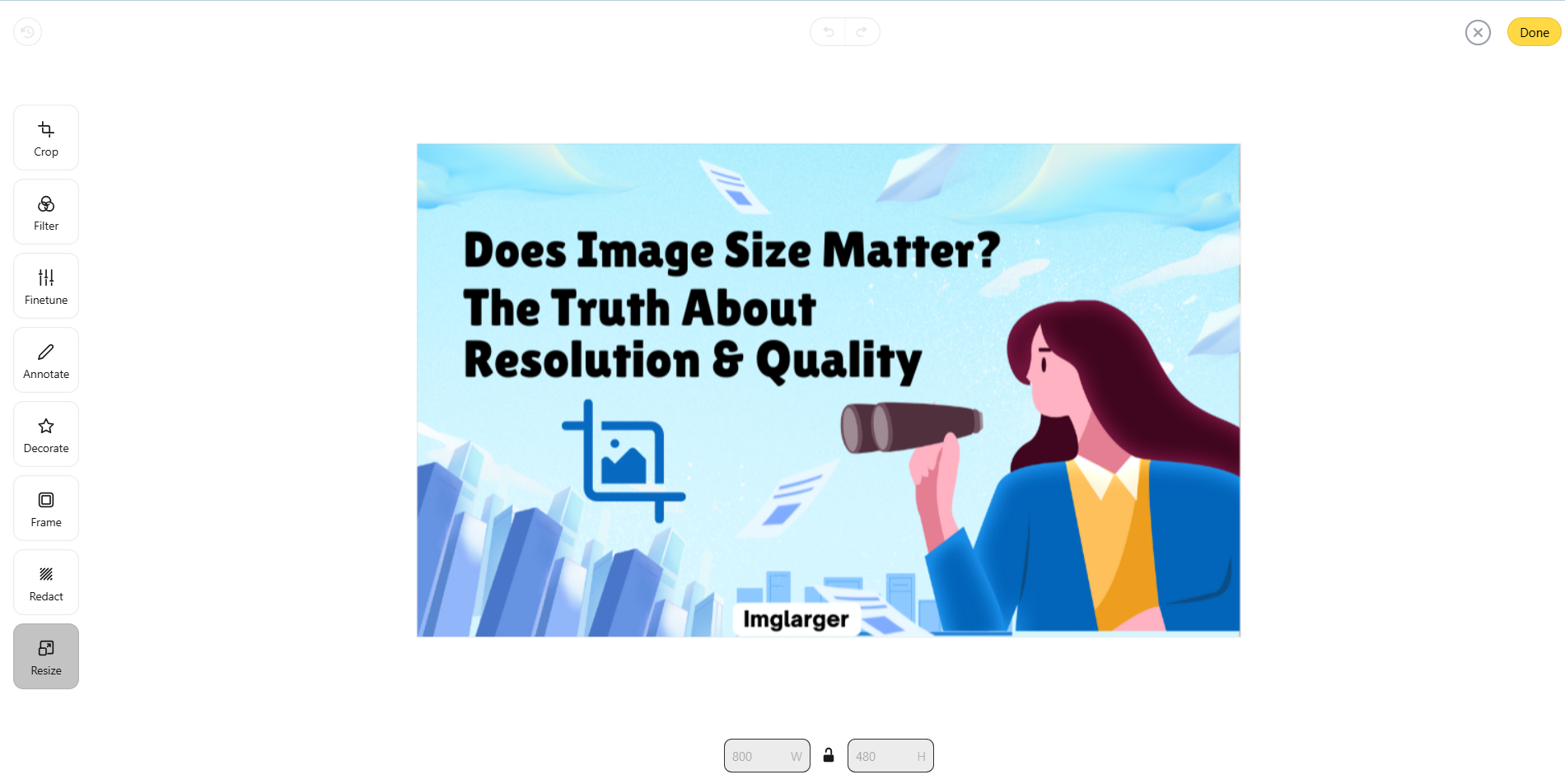
- Step 4: Click the yellow "Done" button in the upper right corner to finish the process, then click the download icon in the upper right corner of the picture in the lower left corner to save it locally.
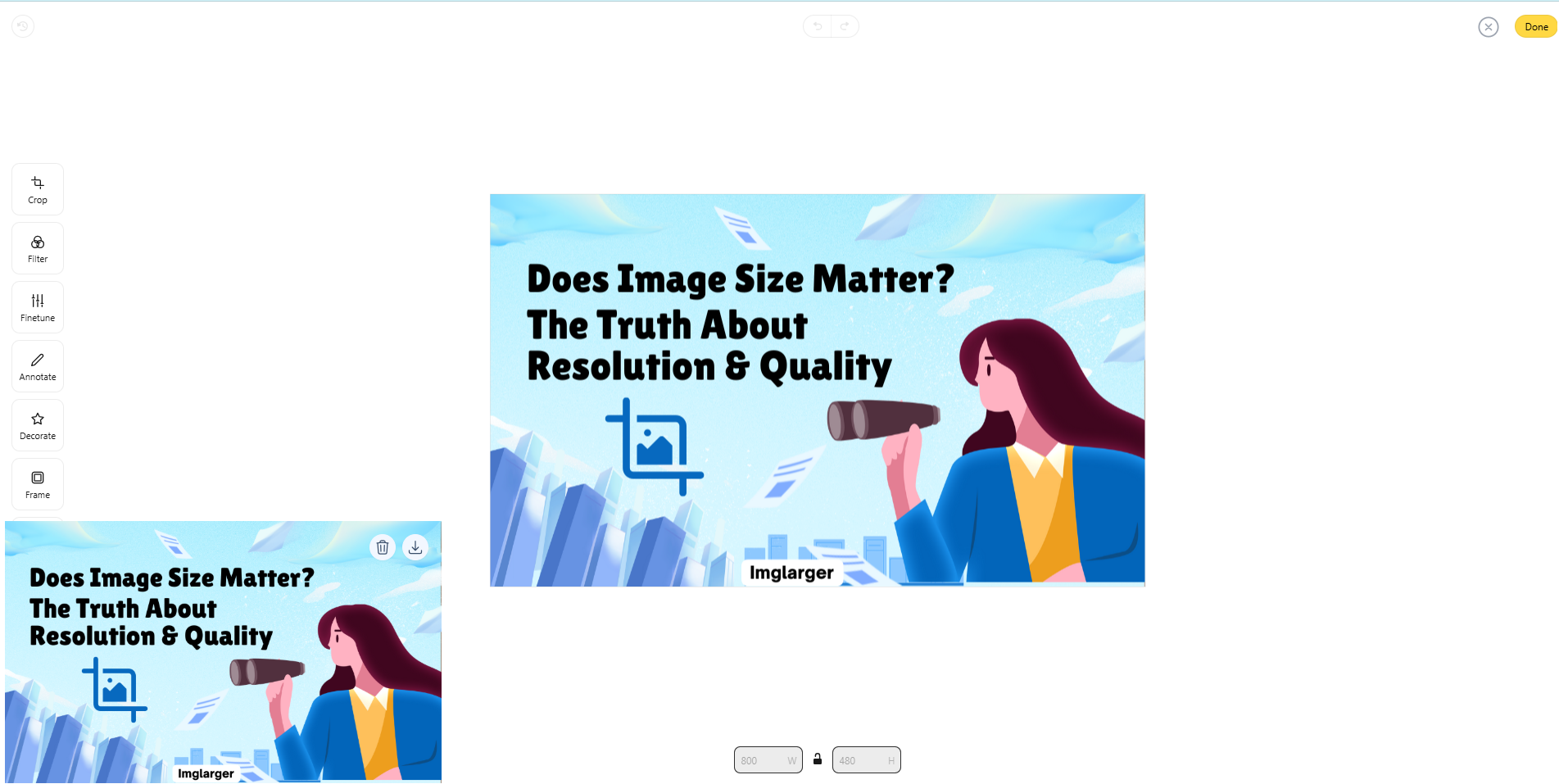
Imglarger is a time-saver for batch resizing, and you can process batches in addition to individual photos. Make your image processing more efficient.
Conclusion
Creating the perfect image requires carefully balancing size, resolution, and quality. An oversized image can degrade performance, while an overly compressed image may lose detail. Finding the right balance ensures the best results on different platforms.
The key is to customize images for their intended use—whether for web, print, or social media. Smaller, optimized files can benefit websites and mobile apps. At the same time, high-resolution images are better for professional printing and large displays.
The golden rule is to optimize without compromise. Use the right file format, compression, and resolution to increase speed and efficiency while maintaining quality. With the right approach, images enhance user experience and performance without sacrificing visual appeal.